Unveiling Ancient Samaria: A Journey Through Time And Age
The quest to understand the "age" of ancient Samaria is a fascinating journey through biblical narratives, archaeological discoveries, and the complex tapestry of ancient Near Eastern history. While the specific query "Samaria J Davis age" does not align with any known historical figure or archaeological data provided, this article will delve into the rich historical timeline and "age" of the ancient city of Samaria itself, drawing exclusively from the provided historical and archaeological insights. Our exploration will reveal Samaria as a vibrant metropolis, a center of power, and a site of profound historical significance, offering a deep dive into its existence across millennia. This comprehensive look aims to shed light on the periods of its prominence, its interactions with neighboring kingdoms, and the enduring legacy it holds in our understanding of the ancient world.
From its foundational years as a royal city to its eventual decline and rediscovery through excavation, Samaria's "age" is marked by layers of human activity, political intrigue, and religious evolution. We will examine how archaeological finds, like the famed Samaria Ivories and the Samaria Hoard, vividly portray its wealth and cultural connections, and how biblical accounts, such as those detailing King Ahab's "ivory house," complement our understanding. Join us as we piece together the historical narrative of this pivotal ancient city, exploring its rise, its challenges, and its lasting impact on the broader historical landscape.
The Ancient Roots of Samaria: A Shared Heritage
Understanding the "age" of Samaria requires us to go back to its very foundations. Samaria was not merely a city but a significant political and cultural entity that played a crucial role in the history of ancient Israel. Its strategic location and fertile surroundings made it an ideal choice for a capital city, eventually becoming the heart of the northern kingdom of Israel.
- Ear Styling Service Near Me
- Paintless Dent Repair Miami Fl
- Estates At Saucon Valley
- New Restaurants In Hawaii
- Dr Michael Lovell
Samaria and Jerusalem: A United Past
In the ninth and eighth centuries B.C.E., Samaria and Jerusalem, though often rivals, shared a profound historical connection. Both cities were integral parts of David and Solomon’s united kingdom of Israel in the tenth century B.C.E. This shared ancestry laid the groundwork for their intertwined destinies, even as they later diverged into separate kingdoms. The common cultural and religious heritage, stemming from the golden age of David and Solomon, meant that despite political divisions, there were underlying similarities in their societal structures, religious practices, and royal traditions. The establishment of Samaria as the capital of the northern kingdom after the split from Judah meant it inherited much of the royal legacy and administrative practices that had been developed during the united monarchy, shaping its early "age" as a distinct but related entity.
The Omride Dynasty and Samaria's Golden Age
The true flourishing of Samaria began with the Omride dynasty. It was during this period that Samaria transformed into a wealthy metropolis, serving as the undisputed center of the Omride dynasty. This era, particularly under kings like Omri and Ahab, marked a significant "age" of prosperity and influence for the city. The Omrides were known for their strong political alliances, particularly with Phoenicia, which brought immense wealth and cultural exchange to Samaria. This period saw significant construction projects, indicating a thriving economy and a powerful centralized government. However, this golden age was not to last indefinitely, as external threats loomed. The Assyrians eventually took over the region, around the late 8th century B.C.E., bringing an end to Samaria's independence as the capital of the northern kingdom. This conquest fundamentally altered the "age" and trajectory of Samaria, marking a transition from sovereign power to a subjugated territory within the vast Assyrian Empire.
Unearthing Riches: The Samaria Hoard and Ivory Treasures
The archaeological discoveries at Samaria provide tangible evidence of its past grandeur and help us determine the "age" of its peak prosperity. These finds offer a window into the daily lives, artistic expressions, and economic power of the city's inhabitants.
- Daniel Yocum Art
- Brow Lamination Lubbock
- Kevin Carroll Katalyst
- Broadway Hot Chicken Middletown Nj
- Delta Gamma Florida State
The Ivory House of King Ahab: Biblical Accounts and Archaeological Echoes
One of the most intriguing aspects of Samaria's wealth is hinted at in biblical texts. The Bible describes King Ahab’s palace as an “ivory house” (2 Kings 22:39). This biblical passage suggests an extraordinary level of luxury and artistic sophistication, which was a hallmark of Samaria's most opulent "age." While the full extent of this "ivory house" is still debated, archaeological excavations have indeed revealed thousands of ivory fragments, confirming the biblical description and providing concrete evidence of such opulence. We know from other biblical passages that the kings of ancient Israel often engaged in monumental building projects, but the mention of ivory specifically highlights a unique level of wealth and access to exotic materials, likely facilitated by the Omrides' strong ties with Phoenicia, a major center for ivory carving and trade. These discoveries help us visualize what the palace of the kings of ancient Israel looked like, particularly during Samaria's most prosperous period.
Deciphering the Ivories: Art, Culture, and Identity
The Samaria Ivories, discovered in 1910 during excavations, created immediate fanfare due to their excellent condition and exquisite craftsmanship. These ivories depict scenes of exotic wildlife and flora, mythological figures, and intricate patterns, showcasing a remarkable artistic tradition. From the moment they were discovered, they presented a puzzle: were they Phoenician or Israelite in origin? Recently, some scholars have challenged the long-held assumption of their Phoenician origin, suggesting they might be Israelite craftsmanship influenced by Phoenician styles, or even directly imported. This debate is crucial for understanding the cultural identity and artistic influences prevalent in Samaria during its peak "age." Regardless of their precise origin, the ivories stand as a testament to Samaria's wealth, its connections to wider trade networks, and the sophisticated tastes of its ruling elite. They are invaluable artifacts for understanding the cultural milieu of the northern kingdom of Israel and the broader ancient Near East.
A City in Flux: Decline, Division, and Rediscovery
The "age" of Samaria is not just about its periods of prosperity but also its challenges, periods of decline, and the eventual re-emergence through archaeological endeavors.
The Shadow of Neglect: Preserving Samaria's Legacy
Despite the invaluable historical insights provided by sites like Samaria, the preservation of these ancient treasures is a constant battle. The "Data Kalimat" notes that thirteen years of neglect threaten the site’s integrity. This highlights a critical issue in archaeology: the ongoing need for funding, protection, and maintenance to preserve historical sites for future generations. Neglect can lead to erosion, looting, and the irreversible loss of invaluable data, jeopardizing our ability to fully understand the "age" and significance of ancient Samaria. Protecting these sites is paramount to continuing our exploration of the past and ensuring that the stories they tell are not lost to time.
The Samaritan Schism: A Deepening Divide
Beyond external threats, Samaria also experienced profound internal and regional divisions. The Samaritan schism, originating in the 6th century BCE, marked a significant religious conflict that led to the eventual permanent separation between Samaritans and Judeans. This schism was characterized by mutual rejection, including marriage restrictions, and deeply impacted the social and religious landscape of the region. This division had long-lasting effects on the perception and reality of Samaria's inhabitants, distinguishing them from their southern counterparts in Jerusalem. The schism represents a critical period in Samaria's "age," defining its unique religious and cultural identity that continues to this day, separate from mainstream Judaism.
Samaria's Place in Wider History: Pilgrimage, Politics, and Puzzles
Samaria's history is intertwined with broader regional developments, influencing and being influenced by pilgrimage routes, political shifts, and enigmatic discoveries that challenge our understanding of its "age."
Navigating Ancient Routes: Avoiding Samaria on the Path to Jerusalem
The geographical position of Samaria also influenced ancient travel and pilgrimage. For Galilean pilgrims seeking to reach Jerusalem, the direct route through Samaria was often avoided due to the long-standing animosity and religious differences stemming from the Samaritan schism. Instead, pilgrims going this way would often take a western route, favoring the coastal plain. This was the longest way for Galilean pilgrims to reach Jerusalem, yet it was preferred to avoid passing through Samaritan territory. This historical detail underscores the deep-seated divisions that characterized the region and how they impacted daily life and religious practice during Samaria's later "age." It illustrates how the schism wasn't just theological but had practical implications for movement and interaction between different Jewish groups.
The Maccabean Era and Regional Transformations
The second century BCE brought significant political upheaval to the region, profoundly affecting Samaria and its surroundings. The Maccabees, initially priests, rose to power and created an independent Jewish kingdom. Their actions reshaped the political map and influenced the "age" of various cities, including Samaria. While the Maccabean focus was primarily on Judea and Jerusalem, their expansionist policies and efforts to establish a unified Jewish state had ripple effects across the entire land of Israel. The Maccabean period saw efforts to Hellenize the region resisted by traditionalists, and the eventual establishment of the Hasmonean dynasty marked a new chapter in Jewish self-rule, impacting the broader context in which Samaria existed, even if indirectly.
Archaeological Windows into Samaria's "Age"
Beyond the direct excavations of Samaria, other archaeological sites offer complementary insights, helping us to contextualize and understand the broader historical environment that shaped Samaria's "age."
Kuntillet ‘Ajrud: Echoes from Beyond Samaria's Walls
Puzzling finds from sites like Kuntillet ‘Ajrud, though not directly Samarian, offer fascinating parallels and insights into the religious practices and cultural milieu of the wider region during Samaria's active "age." The "zingers," two large pithoi, or storage jars, weighing 30 pounds each, discovered at Kuntillet ‘Ajrud, contained inscriptions and drawings that have sparked considerable scholarly debate. These finds provide unique glimpses into ancient Israelite religion, sometimes depicting deities or practices that differ from later normative Judaism. While Kuntillet ‘Ajrud is located in the Sinai, its discoveries shed light on the broader religious landscape of the Iron Age, a period that encompasses much of Samaria's prominence. They contribute to our understanding of the diverse religious expressions that existed across the ancient Israelite kingdoms, including the northern kingdom of which Samaria was the capital.
Samaria in the Broader Biblical and Historical Landscape
Samaria's story is deeply embedded within the larger narrative of biblical archaeology, biblical history, and the study of ancient civilizations. Terms like "ancient Samaria archaeologist," "archaeology review," "bib arch org," "bible history," "bible history daily," "biblical," "biblical arch," and "biblical archaeology" all point to the academic and popular interest in understanding sites like Samaria. These fields continually contribute to our knowledge of Samaria's "age" by analyzing artifacts, interpreting texts, and reconstructing historical events. The continuous research and debate among scholars enrich our comprehension of Samaria's role, not just as a political capital but as a significant cultural and religious center within the ancient world. The ongoing dialogue helps refine our understanding of how Samaria's unique trajectory fits into the grander scheme of ancient Near Eastern history.
The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Samaria
The historical journey of Samaria extends beyond its periods of political power and into later eras, demonstrating its lasting impact. Much as today, Jerusalem was a diverse city and pilgrimage center in the first century C.E., and Samaria, though no longer a capital, remained a significant geographical and cultural entity in the region. The legacy of Samaria's "age" is complex, encompassing its biblical narratives, its archaeological treasures, and the continued existence of the Samaritan community, which traces its lineage back to the ancient inhabitants of the region. The city's ruins continue to yield secrets, inviting further exploration and study.
Samaria's Historical Timeline: Key Periods and Discoveries
To better grasp the "age" of Samaria, here is a summary of key periods and discoveries referenced:
| Period/Event | Approximate "Age" / Century | Significance to Samaria | Reference in Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom of Israel (David & Solomon) | 10th Century B.C.E. | Samaria & Jerusalem part of this kingdom's shared heritage. | "Both were part of david and solomon’s united kingdom of israel in the tenth." |
| Omride Dynasty & Wealthy Metropolis | 9th-8th Centuries B.C.E. | Samaria becomes a wealthy metropolis, center of Omride dynasty. Peak "age" of prosperity. | "Ancient samaria and jerusalem had a lot in common in the ninth and eighth centuries b.c.e", "samaria was a wealthy metropolis, center of the omride dynasty" |
| King Ahab's "Ivory House" | 9th Century B.C.E. | Biblical reference to the palace's opulence, supported by ivory finds. | "king ahab ’s palace is called an “ivory house” (2 kings 22:39)" |
| Assyrian Takeover | Around 722 B.C.E. | End of Samaria's independence as northern capital. | "until the assyrians took over around." |
| Samaritan Schism Origin | 6th Century B.C.E. | Religious conflict leading to permanent separation from Judeans. Defines a unique cultural "age." | "The samaritan schism originated in the 6th century bce" |
| Maccabean Era | 2nd Century B.C.E. | Formation of an independent Jewish kingdom, impacting the region. | "the maccabees created an independent jewish kingdom in the second century bce" |
| Samaria Hoard Discovery | 1910 C.E. | Modern archaeological finding confirming Samaria's wealth. | "The samaria hoard was found in 1910 in excavations" |
| Samaria Ivories Discovery & Debate | 1910 C.E. onwards | Fanfare upon discovery, ongoing debate on origin (Phoenician or Israelite). | "From the moment they were discovered, the samaria ivories created fanfare", "The samaria ivories—phoenician or israelite" |
| Site Neglect Mentioned | Contemporary concern | Highlighting the ongoing challenge of preserving the site. | "However, thirteen years of neglect threaten the site’s." |
Understanding Samaria Through the Ages: A Call to Continued Exploration
The exploration of ancient Samaria is a continuous process, with new discoveries and interpretations constantly refining our understanding of its "age" and significance. The interplay between biblical texts, archaeological evidence, and historical analysis provides a rich tapestry that allows us to visualize this ancient metropolis. From its powerful Omride rulers and their opulent "ivory house" to the complex religious dynamics that led to the Samaritan schism, Samaria stands as a testament to the vibrant and often turbulent history of the ancient Near East. The ongoing efforts by archaeologists and historians, including those associated with "archaeology review" and "bib arch org," ensure that the story of Samaria continues to be told and understood.
The puzzles from Kuntillet ‘Ajrud and the detailed visualization of the Herodian family tree, while not directly about Samaria, provide crucial context for the broader historical landscape in which Samaria existed, especially during the later phases of its "age." These interconnected pieces of information help us appreciate the complexity of the ancient world and Samaria's place within it.
We encourage readers to delve deeper into the fascinating world of biblical archaeology and ancient history. What aspects of Samaria's "age" do you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore other articles on our site that shed light on ancient civilizations and their enduring legacies. Your engagement helps us continue to bring these incredible stories to life and preserve the knowledge of our shared past.
- Alex Decarli Petaluma
- Repeat Offender Clothing
- Tin Christmas Ornaments
- Splash Beach Bar Exuma
- Cedar Crest High School Prom 2025
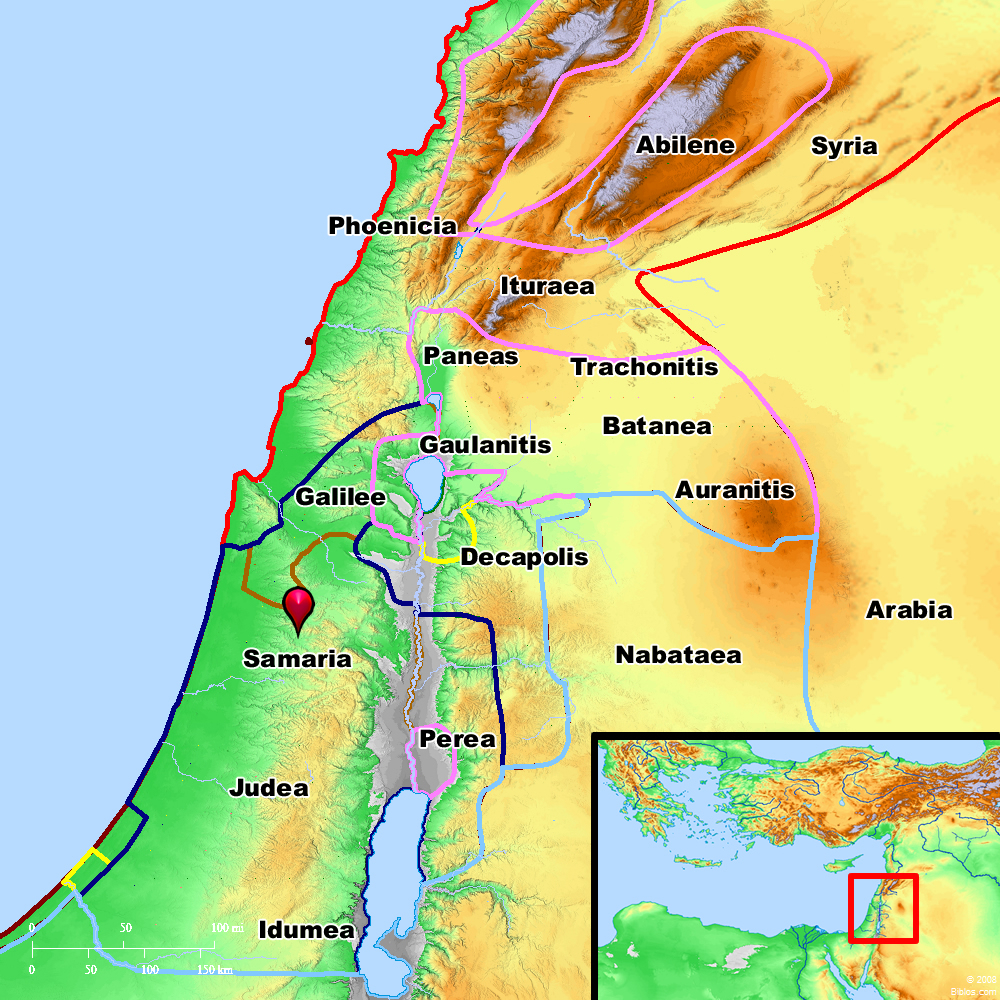
Bible Map: Samaria

Samaria (city) - BibleWalks 500+ sites
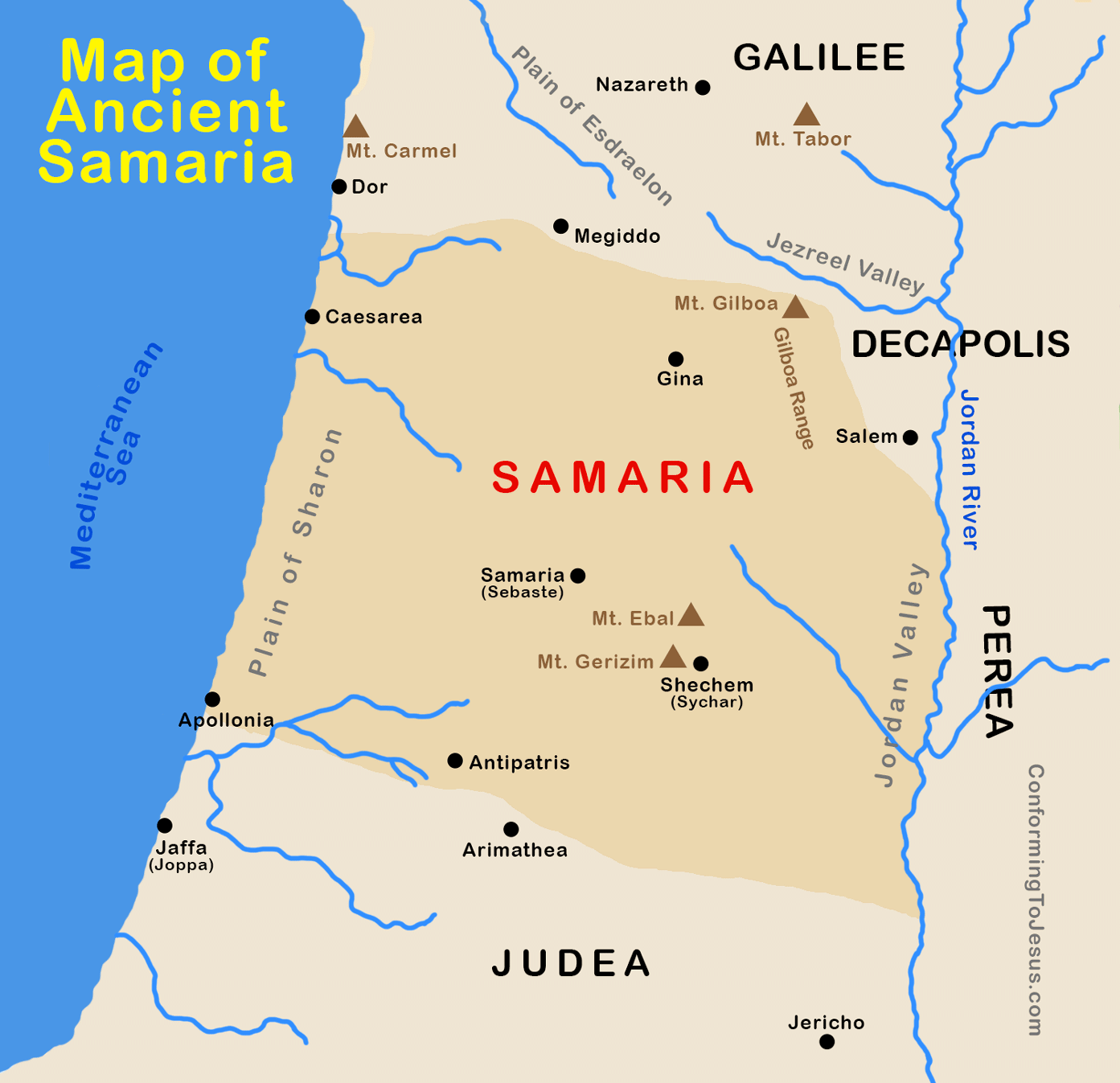
Map of Ancient Roman Samaria - Map of Samaria at the time of Jesus